
Cryptocurrencies can offer numerous advantages to those who understand how to use them effectively. These benefits stem from essential characteristics of cryptocurrencies, including their volatility, liquidity, decentralization, anonymity, and others.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons and methods for utilizing digital currencies, explore the process of acquiring and securely storing cryptocurrency, and examine various popular avenues for generating income through digital coins.
For a more comprehensive understanding of cryptocurrency, its origins, key attributes, as well as its pros and cons, you can refer to the article titled Cryptocurrency for Beginners.
How to use cryptocurrency?
While some individuals remain cautious about digital currencies, others are wholeheartedly embracing them for both personal and business purposes. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which cryptocurrency can be utilized in the modern world.
The first category of applications revolves around transactions. Currently, electronic currencies can be used for worldwide payments, allowing for seamless transactions when purchasing goods from foreign online retailers, for instance.
Furthermore, cryptocurrency can serve as a means of disbursing salaries. In today's remote work environment, many companies are unable to provide employees with cash or card-based payments. Consequently, receiving compensation in cryptocurrency offers a practical solution for such organizations.
The second significant category encompasses various financial transactions, including those designed to generate profits. Let's delve deeper into this diverse group:
- Cryptocurrency investments have gained popularity due to the limited supply of digital currencies. As demand for them increases, their value tends to rise accordingly.
- Another investment avenue is Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), akin to Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in traditional stock markets. Investors contribute funds in the hope of future appreciation in the value of the new coins.
- Trading involves capitalizing on fluctuations in digital currency rates to generate profits. Unlike long-term investments, trading involves numerous transactions over short periods, each yielding incremental profits.
- Deposits (staking) entail placing funds in cryptocurrency on specialized platforms to earn interest, similar to traditional bank deposits. Companies employ your cryptocurrency funds and compensate you accordingly.
- Asset tokenization is the conversion of tangible assets, such as precious metals or real estate, into digital form, enhancing their accessibility and liquidity, thereby making them more easily transferable.
The third category encompasses international payments. Cryptocurrency transfers are conducted directly, without the need for intermediaries like banks or financial institutions, making them an increasingly popular choice for cross-border transactions.
How to utilize cryptocurrency effectively
Now that we've explored the myriad possibilities and benefits of cryptocurrency, let's delve into the essential steps required to begin using it effectively.
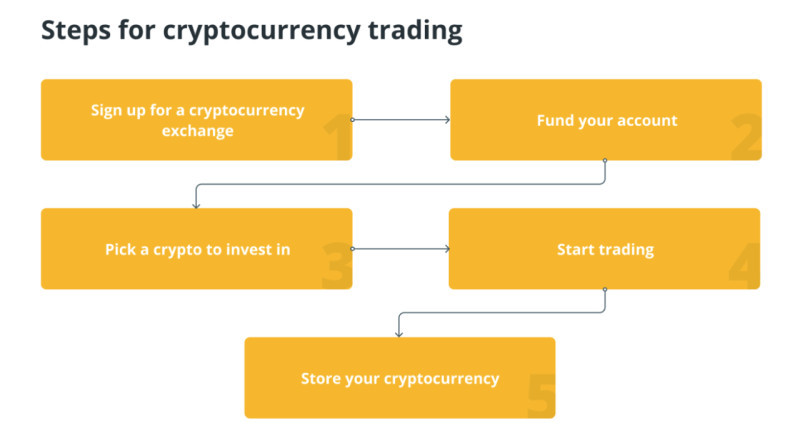
Obtaining a Wallet: To engage in any cryptocurrency transactions, you must acquire a dedicated wallet with a unique address. This address serves as a destination for receiving coins from others. It's crucial to note that each type of electronic currency necessitates a separate wallet and corresponding address.
Acquiring Digital Coins: Digital currencies are typically purchased on specialized platforms known as how to use cryptocurrency cryptocurrency exchanges. Alternatively, you can engage in transactions through specialized exchange services or peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms. While exchanges offer a secure method, they often involve transaction fees. Exchange services facilitate the purchase of cryptocurrency with fiat money, whereas P2P platforms enable direct transactions between users.
Utilization: As previously mentioned, digital currencies serve a wide range of purposes, including payment for goods and services, international online shopping, as well as trading and investment.
Secure Cryptocurrency Storage: Storing your digital coins requires choosing an appropriate wallet. The two main categories are commonly known as "cold" and "hot" wallets. "Cold" wallets are hardware devices without internet connectivity, ensuring enhanced security. "Hot" wallets, on the other hand, are online wallets accessible through the internet.
Exchanging and Selling: All cryptocurrency transactions are conducted on specialized platforms, such as exchanges or trading platforms. Keep in mind that the volatile nature of digital currencies can lead to significant price fluctuations, so the selling price may differ substantially from the purchase price.
How to buy crypto?
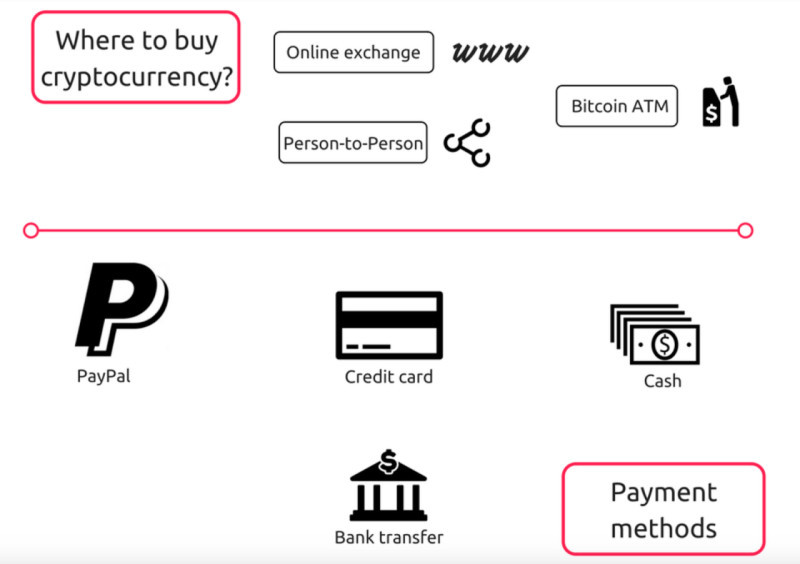
Now let us discuss the methods of buying digital currencies. As already mentioned, there are three ways to buy crypto:
- Cryptocurrency exchanges
- Exchange services
- P2P platforms
To participate in transactions on cryptocurrency exchanges, you must undergo the registration process. Additionally, many platforms require identity verification through the submission of a passport or another form of identification, along with proof of your residence.
How to use cryptocurrency exchanges often provide integrated online wallets, allowing users to receive electronic funds and conduct various transactions and payments with crypto assets.
When selecting a trading platform, it's crucial to consider several factors:
1. Licensing and Company Reputation: Ensure the platform holds a valid license, assess the company's experience in the industry, and explore reviews from real users.
2. User-Friendly Interface: Evaluate the website's interface for ease of use and navigation.
3. Transaction Fees: Take note of the transaction fees associated with buying, selling, and trading on the platform.
One notable drawback of crypto exchanges is the presence of transaction fees. However, these platforms offer enhanced reliability as intermediaries vet each participant.
For those primarily interested in purchasing digital currencies with fiat money, cryptocurrency exchangers are a viable option. Typically, you'll need to provide your bank card details, specify the crypto wallet address for funds transfer, and indicate the desired cryptocurrency amount.
Alternatively, Peer-to-Peer (P2P) platforms facilitate direct transactions between users, eliminating intermediaries. These platforms allow you to browse and select the most favorable offers independently.
One significant advantage of P2P platforms is the absence of transaction fees for cryptocurrency transfers. Think of it as an online marketplace: one user posts an offer to sell a product, and another interested user responds to the ad, simplifying the exchange process.
How to store crypto?
In our previous sections, we've discussed the practical use of cryptocurrency and how to acquire it. Now, let's delve deeper into the vital topic of where and how to securely store your digital assets.
We've mentioned that one option is to keep your funds within a wallet on a cryptocurrency exchange. However, this approach is most suitable when users require immediate access for frequent transactions.
Nonetheless, this method of storage comes with its own set of drawbacks. Cryptocurrency exchanges are frequently targeted by hackers, posing a risk of funds being stolen from user accounts. Additionally, these platforms often impose withdrawal limits on the amounts that can be accessed.
Every cryptocurrency wallet consists of two essential keys: the public key and the private key. Think of the public key as the equivalent of a wallet address, much like an email address. You can freely share this public key with other users, enabling them to transfer digital coins to your wallet.
On the other hand, the private key holds confidential information that must remain undisclosed, akin to an email password. It functions as an electronic signature, essential for confirming and authorizing transactions securely. Guarding your private key is paramount to safeguarding your cryptocurrency holdings.
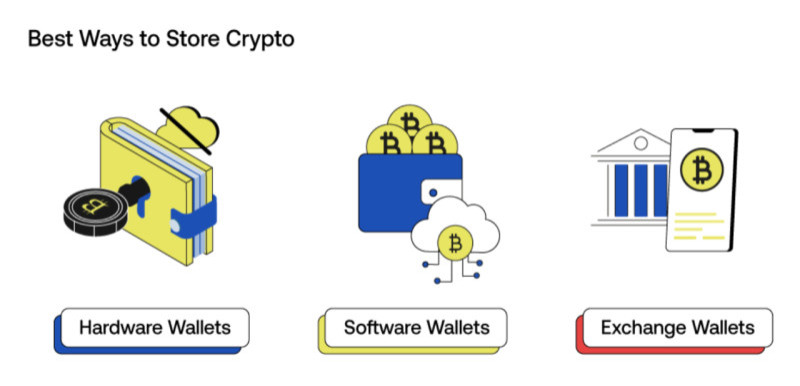
Broadly, there are two primary categories of wallets designed for safeguarding cryptocurrency:
1. Custodial Wallets: These are specialized services offered by third-party providers. In custodial wallets, both the wallet itself and the assets within it are under the complete control of the service provider, including the management of the private key. One common example of this is the wallets provided by cryptocurrency exchanges.
2. Non-Custodial Wallets: These wallets empower users to independently store and maintain control over their private keys. Non-custodial wallets come in two main forms: software wallets, which are software applications, and hardware wallets, which are physical devices like USB drives.
Non-custodial wallets are generally regarded as more secure, primarily because they are not connected to the internet and are less susceptible to hacking attempts. However, it's vital to note that if you ever lose the password or other crucial data associated with non-custodial wallets, recovery can be exceptionally challenging compared to custodial ones.
While custodial wallets offer greater ease of use, operating in a manner similar to standard online accounts, non-custodial wallets can appear more complex, especially for beginners. Additionally, users of non-custodial wallets bear the responsibility of ensuring the secure storage of their secret keys and other essential data.
Exploring crypto investments
Now, let's delve into the intricacies of generating income through digital currencies. One of the favored approaches in the world of how to use cryptocurrency is the art of investment, commonly referred to as HODLing.
As previously mentioned, electronic currencies are issued in limited quantities, rendering them immune to the effects of inflation. This scarcity contributes significantly to the consistent appreciation of their value, driven by the increasing demand coupled with finite supply.

In the realm of digital currencies, there are primarily two avenues for investment: buying and holding coins or investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Let's delve into each of these approaches for a more comprehensive understanding.
1. Buy and Hold (HODL):
One approach involves acquiring digital coins with the intention of holding onto them for an extended period, typically around 3-5 years, with the goal of witnessing their value appreciate over time. The potential profitability in such investments is virtually limitless, as many digital currencies have demonstrated consistent growth.
However, substantial profits often require a sizable initial investment. If your starting capital is relatively small, your profitability may resemble that of traditional stock investments.
Additionally, there's the possibility of investing in newly emerging coins. Nevertheless, this comes with elevated risks, as some may vanish quickly, while others might turn out to be fraudulent schemes aimed at defrauding users.
2. Investment in Cryptocurrency Funds:
The second option involves purchasing shares or units in funds specifically tailored for how to use cryptocurrency investment. This approach simplifies the process considerably, as you are not required to analyze the market or select assets for investment – the fund assumes this responsibility.
Profits generated by the fund are distributed among its shareholders in proportion to their contributions. Fund managers receive compensation in the form of commissions from all participants for their services. Importantly, investors have the flexibility to sell their shares or units at any time.
Trading
Another way to benefit from cryptocurrencies is active trading. It is radically different from the method described above; we will consider it in more detail in this section.
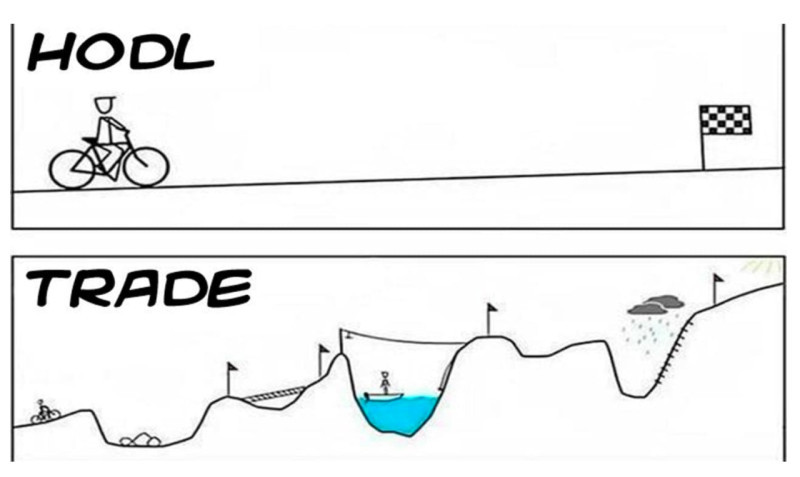
Unlike investing, where long-term transactions are made with the expectation that the value of coins will increase after several years, trading capitalizes on any fluctuation in coin value, sometimes within a single day.
To engage successfully in trading, one must possess the ability to analyze the market, interpret charts, and discern opportune moments for transactions. It's essential to gauge the popularity and demand for a coin, its trading volumes, and historical data.
These skills can be acquired autonomously or through training courses, but mastering them and gaining practical experience takes time.
Trading typically involves numerous short-term transactions aimed at generating small profits from each. Positions can be initiated for both buying and selling cryptocurrencies, depending on market conditions.
The fundamental principle for traders is to buy at low prices and sell at high ones. However, identifying the optimal points for buying and selling isn't always straightforward. At times, it may appear that a currency has hit its minimum value, only to plummet further, or conversely, the value may be on the rise, prompting a trader to sell, yet the price continues to climb for cryptocurrencies.
One challenge with cryptocurrencies is the difficulty in predicting their value direction. Unlike traditional currencies, the factors influencing their rise or fall differ, making prediction more complex.
Staking
Staking is another popular way of making money from digital currencies. It consists in users storing their coins on special platforms or wallets for a fee.
The platform can use these funds for various purposes: maintaining the network, creating new blocks or carrying out any operations. For the owner of coins, such storage allows him to receive additional digital assets.
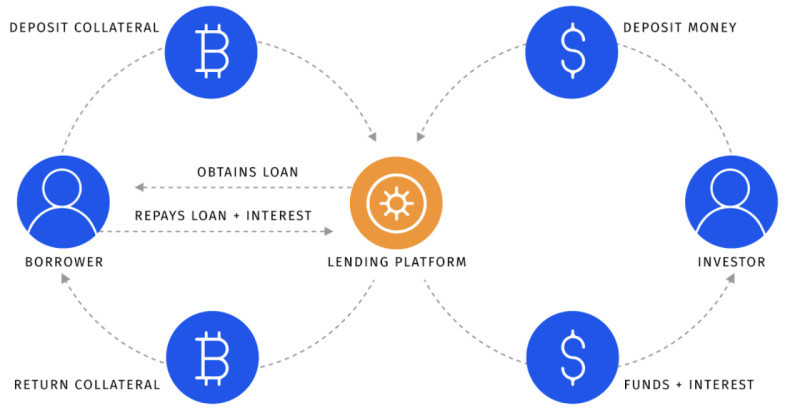
At its essence, staking mirrors a bank deposit scenario, where funds are entrusted to the bank with the expectation of earning interest. The bank employs these funds for its operations, and upon a specified duration, the client retrieves the initial deposit along with the accrued interest.
Various forms of staking exist:
1. Fixed: Rewards, either as a fixed percentage or a set number of coins, are granted to the cryptocurrency owner after a predetermined "locking" period of their funds.
2. Flexible (perpetual): Cryptocurrency owners can partially or fully withdraw their funds throughout the staking period without affecting potential profits.
3. Liquid: Deposited coins can serve as collateral or a guarantee for securing a loan or other purposes.
4. Delegated: Coins are entrusted to another user, who undertakes the staking process with them, and both parties share the resulting rewards.
Importantly, different digital coins may impose distinct staking conditions, such as varying interest rates, deposit sizes, and so forth. Additionally, each network enforces its own rules regarding the "unfreezing" of assets.
While some networks permit coin withdrawal at any time, others require a predefined duration, which could extend up to a year. Minimum deposit thresholds and storage procedures may also be specified.
Among cryptocurrencies, Ethereum stands out as a prominent choice for staking. Despite its comparatively modest returns, this coin garners trust among investors for its reliability.
Determining potential earnings
We've extensively discussed the allure of digital currencies, but let's delve into the specifics of potential earnings. Now that we've explored how to use cryptocurrency operates and the various avenues for profit, let's examine concrete figures.
There's no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of potential earnings. Much hinges on how users engage with digital currencies, their initial investment, and the timeframe set for profit generation.
Active income-generating methods, such as trading or coin mining, may yield varying returns. They demand user participation, significant time investment, and, in the case of mining, financial outlay.
Earnings from trading are influenced by numerous factors: choice of trading platform, trading strategy, adeptness in capital and risk management, market analysis proficiency, and the time commitment dedicated to trading.
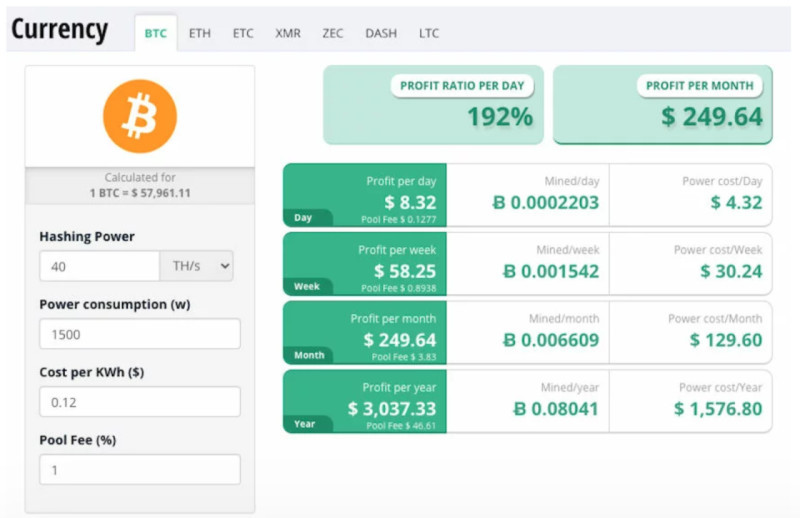
If you embark on solo mining, you can expect to pocket around $500 to $1000 monthly. However, pooling resources and establishing mining farms prove far more lucrative, potentially yielding earnings ranging from $3500 to $5000.
Moreover, passive income opportunities abound. A prime example is investing in cryptocurrency deposits. Returns from such investments can surpass 10% annually, contingent upon the selected coin and platform.
As reiterated multiple times, digital currencies exhibit consistent, gradual appreciation. Consequently, allocating even a modest sum for a five-year period can yield substantial returns. Patience remains paramount in such endeavors.
Certain staking platforms tout returns of up to 100%. However, it's crucial to note that such elevated returns correspond with heightened risks, and instead of reaping profits, one might incur losses. In such scenarios, opting for stablecoins, whose value is tethered to fiat currencies, offers a safer alternative.
How to sustain crypto engagement
The allure of the digital currency market draws in a plethora of individuals, yet not all grasp the intricacies of cryptocurrency usage. Consequently, many enter the market swiftly, deplete their savings, and depart just as hastily.
To avert such outcomes, one must comprehend the nuances of electronic money and factor in associated risks. A pivotal characteristic of crypto is its pronounced volatility, wherein coin values can fluctuate by double-digit percentages within a single day.
This volatility presents both opportunities and pitfalls. On one hand, it offers traders the potential to amass profits swiftly. Conversely, inexperienced users lacking a firm grasp of optimal entry and exit points may swiftly deplete their deposits.
Seasoned users employ a Stop Loss order to mitigate such risks. This mechanism automatically terminates transactions once an asset reaches a predefined minimum value, safeguarding users from further losses amid declining asset values.
Another notable risk stems from selecting the wrong coin. With myriad digital currencies in circulation, the temptation to invest in obscure yet ostensibly promising projects abounds. However, many such ventures are short-lived or outright fraudulent.
Fraudulent schemes warrant special attention in the crypto market. Unscrupulous entities fabricate counterfeit trading platforms and applications, luring individuals with promises of exorbitant profits before vanishing into thin air.
Virtual wallets also constitute prime targets for malevolent actors, particularly "hot" wallets on crypto exchanges susceptible to hacking. Losing wallet passwords can pose significant challenges for recovery, underscoring the importance of securely storing such credentials.
The psychological aspect, particularly for novices, should not be underestimated. Greed and fear of missing out wield considerable influence over inexperienced users eager to swiftly amass wealth. Conversely, seasoned users develop and adhere to disciplined trading strategies.
Conclusion
Digital currencies have gained considerable traction, finding utility in both commercial and personal spheres. This article has explored the essential facets of cryptocurrency usage and profit generation.
Presently, electronic money facilitates international transfers, payments for goods and services, and serves as a means to generate income. There exist several primary avenues for profiting from how to use cryptocurrency, each with varying levels of user involvement.
For active participants, options such as mining or trading, which necessitate proactive engagement, prove suitable. Mining involves the creation of new coins, while trading entails speculative transactions.
Alternatively, those seeking to earn income with minimal effort can explore passive income methods. These include investments and staking. In the former, cryptocurrencies are purchased and stored in wallets for extended periods to capitalize on value appreciation.
Staking operates akin to a deposit, wherein funds are transferred to specialized platforms or services and "frozen" for a specified duration. In return, the coin owner receives rewards in the form of a percentage or fixed amount.
Regardless of the chosen method, it's crucial not to approach cryptocurrency profit generation lightly or anticipate quick gains sans stress. Such expectations are unrealistic and may render one susceptible to exploitation by scammers. Therefore, diligent research and prudent decision-making are imperative.
You may also like:
What is Cryptocurrency Used for
What Cryptocurrency is Backed by Gold
When was the First Cryptocurrency Created
How to Make Money on Cryptocurrency
How to Make Money on Cryptocurrency without Investment
How-to Make Money on Cryptocurrency with Minimal Investment








 Back to articles
Back to articles

