
Hardly anyone is unaware of digital currencies and the possibilities they provide. Yet, many continue to distrust cryptocurrency because it cannot be physically held or touched.
To feel more assured on this topic, it's crucial to get an insight into it. In this article, we'll discuss cryptocurrency, its key features, and how the entire mechanism of transferring coins from one user to another operates.
To learn more about various types of cryptocurrencies, how they appeared, their development, advantages, and disadvantages, you can refer to the article "Cryptocurrency for beginners."
Features of cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency possesses several features and characteristics that distinguish it from any other currencies and monetary units. Let's examine in more detail what makes cryptocurrency unique and how it can be utilized.
- Lack of a physical equivalent. Crypto is entirely digital currency. It exists only in virtual space, and although it cannot be touched, it can be used as a means of payment and exchange.
- Anonymity. When using digital money, it's impossible to trace who transferred money and where it was sent. While the transaction amount is publicly accessible, all other information is hidden thanks to a special technology for encoding information – cryptography.
- Decentralization. There is no single authority or country that controls the issuance and circulation of digital money. However, at the local level, states and their bodies regulate the circulation of digital currencies in their countries.
- Inflation resistance is largely achieved due to decentralization and the absence of influence from the banking system. It's impossible to "print" more crypto and thus affect its rate.
- Direct Transactions. Conducting transactions with digital money does not require a third party, such as a bank or another financial institution. Operations are conducted directly between users.
- Security. The reliability of the blockchain, the network in which crypto circulates, is ensured by a well-encrypted security system. Hence, in more than 10 years of digital currencies' existence, no one has managed to hack this system.
Insight into blockchain
We've discussed the fundamental features of digital currencies. Yet, to understand how cryptocurrency functions, it's crucial to grasp what blockchain is and how it's structured.
Blockchain is a specialized system composed of blocks of information, where data about all cryptocurrencies and transactions with them are recorded and stored. Each entry made into the system is encoded in a specific way, making it impossible to alter or delete.
One of blockchain's most important characteristics is that information is stored on a distributed ledger. This means that all data is not located on a single person or organization's computer but across a multitude of independent devices connected via the Internet.
Thus, even if information is lost on one or several computers, it remains on other media. This feature makes it impossible to forge blockchain records. Indeed, if an entry does not match the records on most other devices, it will be deemed incorrect.
Each block consists of a certain number of records. Then, blocks are sequentially linked into a chain, which is referred to as the blockchain. This chain is unbreakable, as each subsequent block contains a reference to its predecessor.
However, this system couldn't function without special individuals – miners. These people perform some of the most crucial functions:
- adding new blocks to the network;
- storing copies of the blockchain;
- confirming currency transactions;
- verifying transactions;
- mining new coins.
The number of miners working in a single network can be unlimited. The more miners there are, the more secure the network is considered. Mining requires special equipment and software.
For their work, miners receive rewards – commissions from all transaction participants, as well as from the network itself. Their reward is also in crypto, credited to their accounts, thus increasing the total volume of digital currencies.
More on distributed ledgers
As we've already discussed, the uniqueness of information storage in blockchain lies in the fact that it is not stored on a single server or computer of any one organization, but across an entire network of computers.
These servers are also called nodes, and their number can reach several thousand in a single network. For example, the Bitcoin network has over 15,000 nodes, and anyone can launch their own node if they have the necessary equipment and software.
The network's server source code is open, and every node that connects to the network automatically downloads all the transaction data conducted within it, synchronizing with other nodes.
Then, when a new transaction is conducted, it is also recorded simultaneously on all servers. The record is entered into a block, and the blocks are combined into a chain. This chain contains data about all crypto transactions since its inception in 2009.
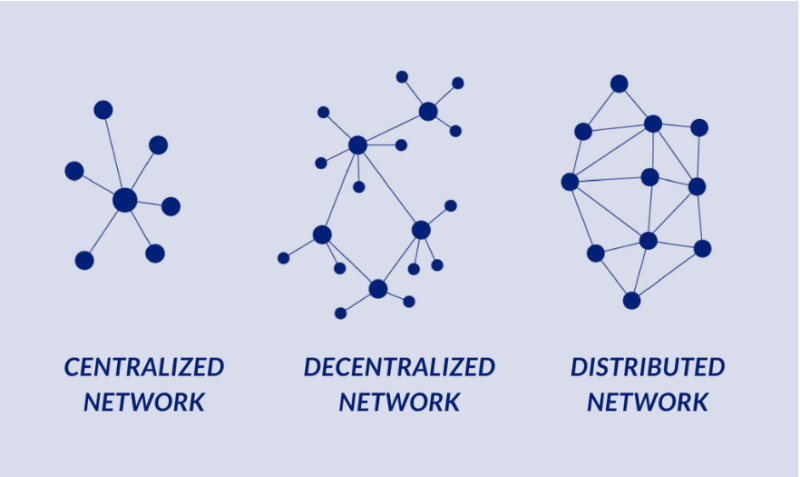
One of the characteristics of distributed ledgers is decentralization, as the information is stored on independent servers located around the world. However, there is another important concept that characterizes them – consensus.
All network nodes constantly interact with each other to reach a majority consensus. If for some reason some nodes were not online during the transaction, the operation is considered valid if it is recorded by the majority (i.e., 51% of servers).
Subsequently, when nodes are turned on, the information is synchronized on them. Thus, even the switching off of several servers from the network does not disrupt its functioning.
How does cryptocurrency work
A transaction made with digital currency is like an email message, digitally signed and sent across the network for confirmation. All operations are public and can be found in the ledger book, i.e. the blockchain.
Like any other transaction, a cryptocurrency transaction involves two parties: the seller and the buyer. However, there are nuances to consider. Let's delve deeper into the specifics of conducting transactions with crypto.
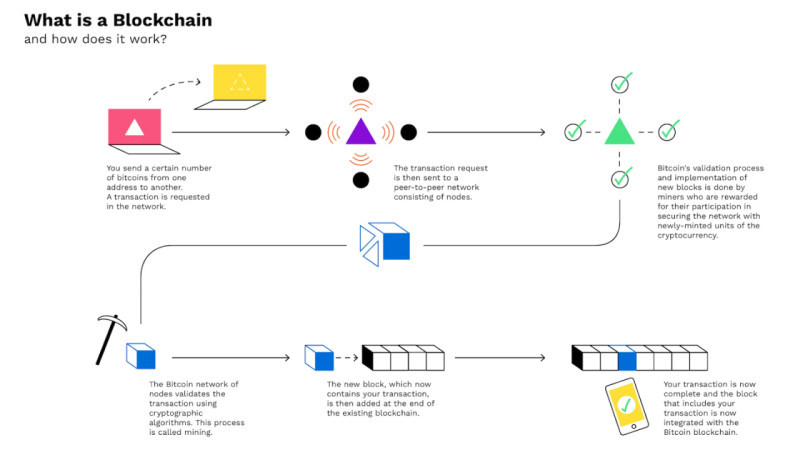
As mentioned, there are no intermediaries in transactions with digital currencies. However, this means there is no control over them. The network and the correctness of transactions are monitored by miners.
When a user wants to sell cryptocurrency, a record is made in the blockchain. The system then uses complex mathematical algorithms to verify whether the user indeed possesses the amount of digital currency claimed.
If the information about the digital funds is confirmed, the transaction is entered into the ledger. The sender can no longer transfer these funds to anyone else as they have now moved to another user.
To conduct any transaction, a user needs two keys: a public or open key and a personal or private key. The public key is also known as an address, similar to an email address or a social media name.
It consists of a sequence of letters and numbers and is publicly available, so it can be shared with others. The address can be given to others so they can send digital money to the user.
The private key is also a sequence of letters and numbers, but it functions like a password or digital signature, so it must not be shared with anyone. It must be kept in a secret place. The personal key provides access to the user's crypto.
More on crypto transactions
We've established that all operations conducted with digital currencies are records entered into a special ledger, the blockchain. To better understand how does cryptocurrency work, let's examine the features of such operations.
All transactions with digital money are public. Once a transaction is signed digitally and confirmed, it is recorded and fixed across the entire network.
The processing time for each operation can vary, depending on the network's load at the moment. On average, processing a single transaction takes 20-60 minutes, but this time can significantly increase during periods of high traffic.
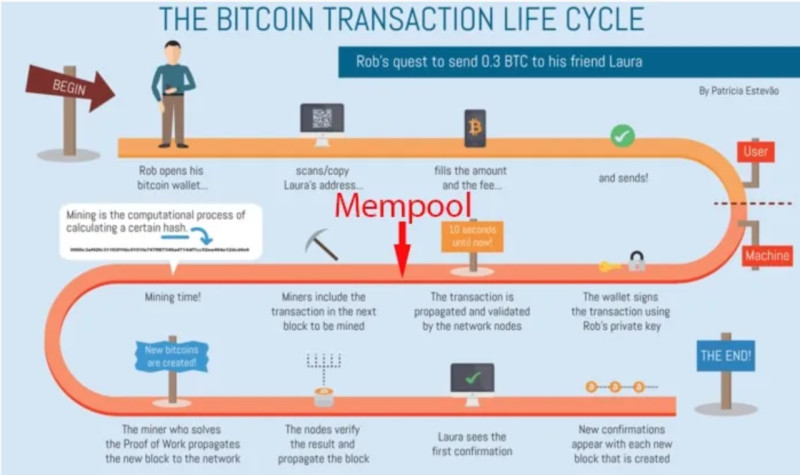
Unconfirmed transactions are put into a special queue - the mempool. In this case, a transaction can be rejected or not used by miners. One reason could be an excessively low fee, especially when the network is overloaded.
If a transaction is rejected, it is removed from the mempool and does not appear in the blockchain. The currency intended for transfer to another user remains in the sender's wallet.
If the operation is confirmed by miners and added to a block, it remains in the blockchain forever. To change even one transaction already recorded in the blockchain, all subsequent blocks would need to be recreated.
However, it is possible to reverse a transfer sent to the wrong address. For this, both the sender and receiver must enter a password. Such transactions are conducted on special wallets.
How cryptocurrency works in simple terms
To better understand cryptocurrency transactions, let's compare it to a more familiar and conventional method of payment - opening a bank account.
When a user opens an account in a bank and subsequently carries out any operations, this information is inaccessible to anyone other than the person and the bank. No one can know where the money on this account is coming from or going to, except for law enforcement requests.
To transfer money to another person's account, you need to know their account number or the number of the card attached to that account. However, even with this information, the sender does not learn how much money is in the recipient's bank account or what operations they have carried out.
Moreover, every such transaction involves an intermediary - the bank, which processes operations and ensures their correct execution. Essentially, these transfers are also conducted electronically: the amount is debited from the sender's account and credited to the recipient's, without any physical exchange of money.
In terms of digital currency operations, transactions also occur by merely changing the balances of the parties involved in the deal without the transfer of any physical assets.
However, there is no intermediary here: transactions are conducted directly between the recipient and the sender. All transactions are added to a vast network, consisting of over 15,000 servers (for the Bitcoin network), and are accessible to the public.
This means that with special resources, anyone can view any cryptocurrency transactions happening anywhere in the world. The information available includes the transaction amount and the wallet addresses of the sender and recipient. However, no personal information is disclosed.
What is cryptography
As mentioned repeatedly, cryptocurrency transactions are characterized by security. This is ensured through a special data encryption technology - cryptography. But cryptography is not only used in blockchain. Let's delve into what this technology is and how it is used.
Cryptography encompasses various methods of encrypting information. Special algorithms are used to protect data by identifying and eliminating vulnerabilities.
Cryptography is applied in various fields, including banking, accounting, information security, and any operations conducted over the internet.
The essence of cryptography is that any original message or record is encrypted and can later be decrypted using a special key. For those who do not possess the key, the data appears as a mere set of symbols.
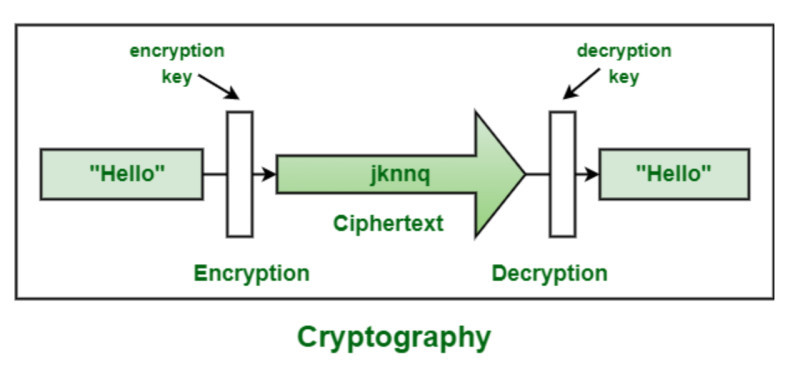
There are two main groups of algorithms used in encryption:
- Symmetric, which are based on a single key for both encrypting and decrypting the data. These algorithms are used in bank transfers and online payments. Their downside is the potential interception of the key and access to all data.
- Asymmetric have two keys: a public and a private one. The sender encrypts data using the public key, and the recipient can decrypt it using their own private key. Therefore, stealing one of the keys is futile.
Blockchain uses asymmetric encryption algorithms. As mentioned, there are two keys: a public and a private one. Besides the keys, blockchain has another layer of protection.
Every block is verified by all network participants. Once data is entered into it, it cannot be changed. To alter even one record in one block, it would need to be done across all network servers, which is impossible.
How to avoid falling victim to scammers
The immense popularity of digital currencies attracts heightened attention from scammers. However, understanding how does cryptocurrency work can help users avoid falling for their tricks. Despite the high level of security for electronic money and transactions, scammers constantly develop new methods to exploit credible users.
Let's look at the main methods scammers use and how to protect yourself from fraudulent schemes.
- Fake websites. Unscrupulous users create platforms that supposedly allow trading in crypto. However, no actual transactions take place, and scammers simply take users' money.
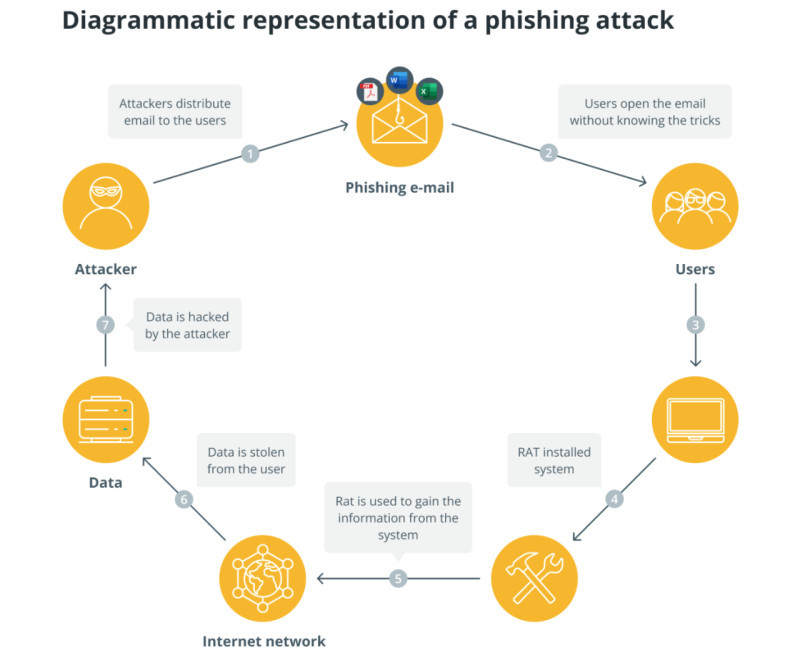
- Phishing is a type of fake website that visually mimics real sites or platforms. They may also send emails asking you to click on a link to a specially created site and enter your secret key.
- Fake applications are analogous to websites that are downloaded to smartphones. When such applications appear in marketplaces, they are quickly removed, but they often lead to losses.
- Free giveaways. Scammers offer to send them a certain amount of digital money so that they can multiply it in a short time.
- Launching new coins is a fraud involving raising capital supposedly for launching a new type of crypto. Many go as far as renting offices and hiring staff to make everything look as convincing as possible.
- Cloud mining is a service that allows mining crypto by renting equipment. Scammers use such schemes to lure funds from users.
How to recognize fraudulent schemes and not fall for these tricks? Let's look at the main safety rules for conducting transactions with cryptocurrency in the next section.
Cryptocurrency usage rules
To protect your cryptocurrency assets from fraudulent attacks, it's important to know not only how cryptocurrency works but also how to handle it properly. We've compiled the main rules and tips for working with digital currencies.
Use only reliable trading platforms. When choosing a resource for cryptocurrency transactions, check its regulation, how long it has been in the market, and read user reviews. Establish direct contact with the exchange before transferring money.
Choose well-known currencies. Investing in a new project and making a substantial profit sounds tempting. Many of these new projects often turn out to be scams. Even genuine startups can quickly disappear.
Don't invest large amounts immediately. Even if you have significant capital but lack experience in trading crypto, don't invest a lot all at once. Digital currencies are a special asset that requires a serious and thoughtful approach.
Verify apps and websites for cryptocurrency transactions. As we mentioned, fraudulent sites and apps can visually match the real ones, so check them thoroughly before starting to use them fully.
Protect your assets. For storing acquired coins, it's better to use special devices that do not connect to the internet. In such cases, it's practically impossible for scammers to access them.
Take your time. Often, mistaken decisions are made in haste. Scammers pressurize, promising significant profit for immediate participation ("limited offer", "only now") to prevent you from thinking it over.
Don't be swayed by advertisements. Scammers actively promote their offers on social networks and may illegally use images of media personalities.
If you still fall for scammers' tricks and make a payment or disclose any personal information, immediately contact your bank. Also, urgently change all passwords and access to your personal account data. Additionally, report the fraud to law enforcement agencies.
Conclusion
In this article, we've explored the key issues related to how does cryptocurrency work, how transactions are made, and the security of the blockchain where currencies are traded. Despite digital currencies not having a physical counterpart, they are considered the most secure. Every transaction made with crypto is recorded in a special ledger – the blockchain, where it's impossible to alter or delete this record.
While the market for digital currencies is decentralized, this does not mean it is unregulated. Each network is maintained by special individuals – miners, who add new blocks to the network, verify information, and mine new coins.
When any transaction is made with crypto, a new record is created in the network. The system then verifies the accuracy of the data, and only after that, the transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain.
Information about digital coins and transactions with them is stored on thousands of independent servers, combined into one network. Therefore, even if a record is falsified on one or several devices, it remains correct on all others.
A special method of encoding – cryptography – is used to protect data. To make any transaction, users require two keys: a public and a private one.
You may also like:
What is Cryptocurrency Used for
What Cryptocurrency is Backed by Gold
When was the First Cryptocurrency Created
How to Make Money on Cryptocurrency








 Back to articles
Back to articles

